What is a joint?
Regions in the body where a connection is made between bones and the body is a joint. These are the areas where movements occur. These movements vary in type and degree.
The joints are classified structurally and functionally.
The most complex joint in our body is the knee joint.
The weakest joint in our body is the shoulder joint.
Conditions occurring at joints
- Osteoarthritis – bones rub together, causing swelling and stiffness
- Rheumatoid arthritis – autoimmune disease, inflammation at joint
- Gout – swelling and pain
- Bursitis – swelling and irritation of bursa (fluid sac around the joint)
- Osteoporosis – bones become fragile (weak)
- Dislocations – injuries causing bone to move from its position
Types of movements
- Flexion – bending of the joint
- Extension – straightening the joint
- Abduction – movement away from midline of the body
- Adduction – movement towards the midline of the body
- Rotation – circular movements around a fixed joint
- Plantarflexion – Pointing the toes downwards
- Dorsiflexion – Pulling the toes up
- Circumduction – multiple movements at one particular joint
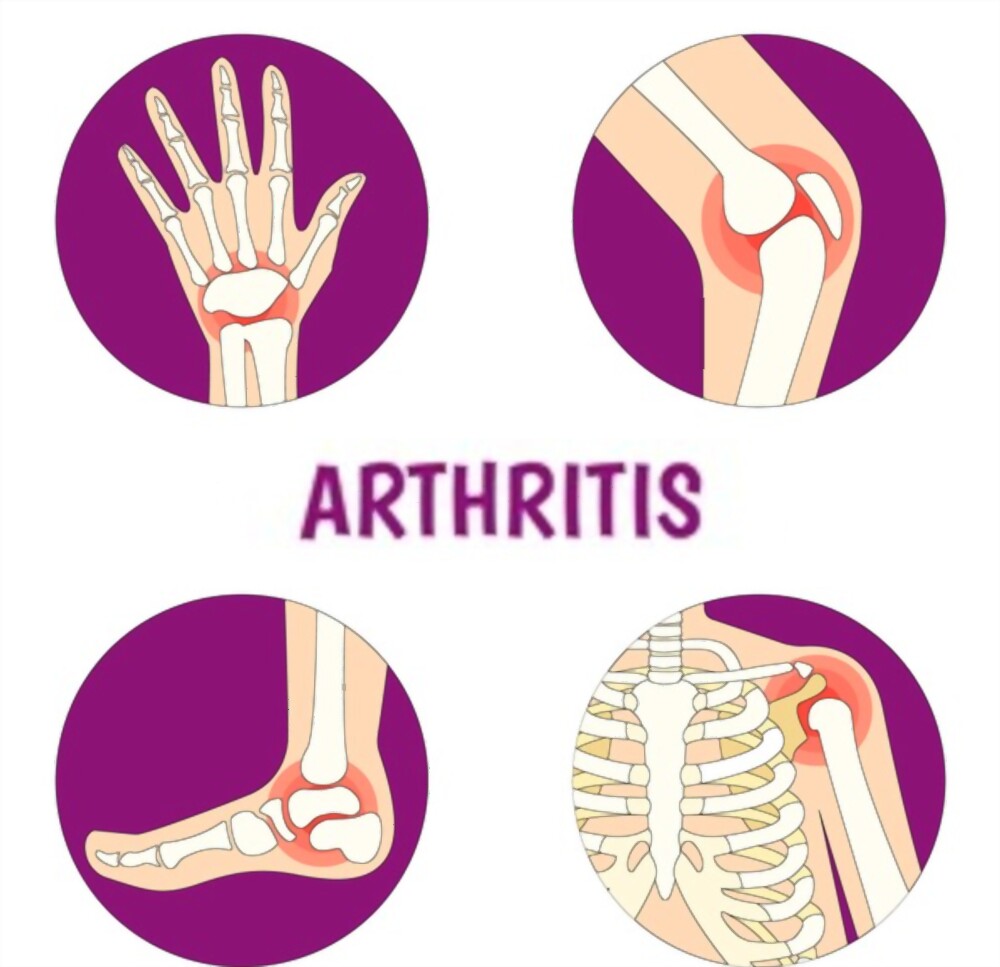
What is Arthritis?
Inflammation at joints causes arthritis. Arthritis can occur at one joint or multiple joints at a time.
It has 2 major types, namely-
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
1. Osteoarthritis
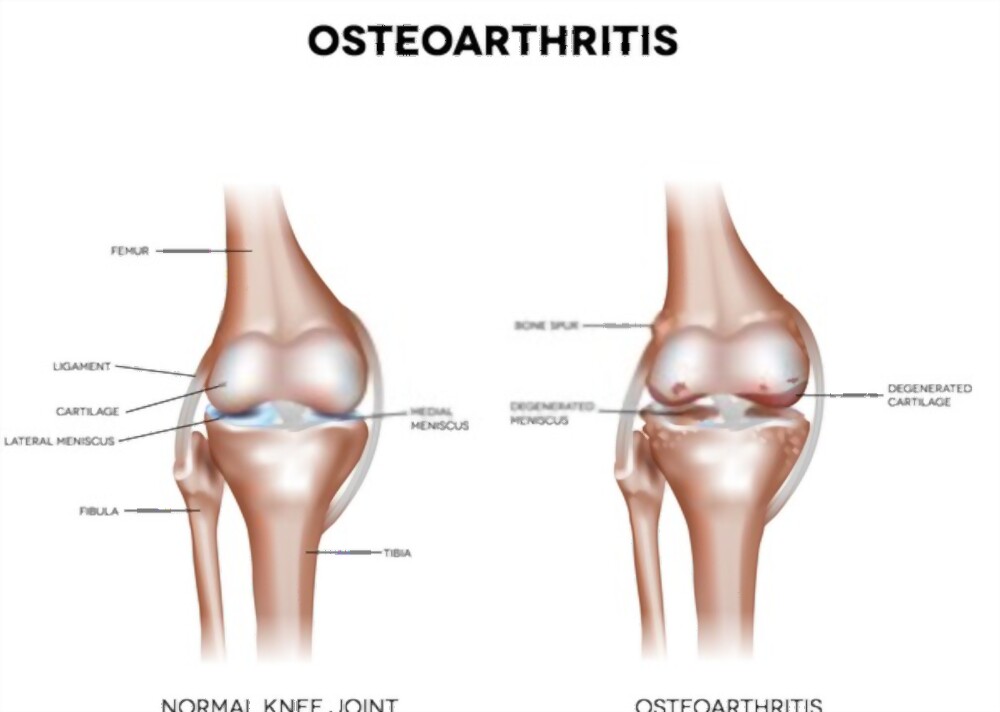
The most common type of arthritis is Osteoarthritis.
Caused by Wear and Tear damage of the joint’s cartilage.
Cartilage is like a cushion at the end of bones. It reduces friction during joint movements. Hence, it provides frictionless movements.
Severe damage can lead to direct grinding on the bone. This causes pain and restricted movement.
This affects the entire joint. There is inflammation in the joint lining. There are changes in the bone, the connective tissue deteriorates.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
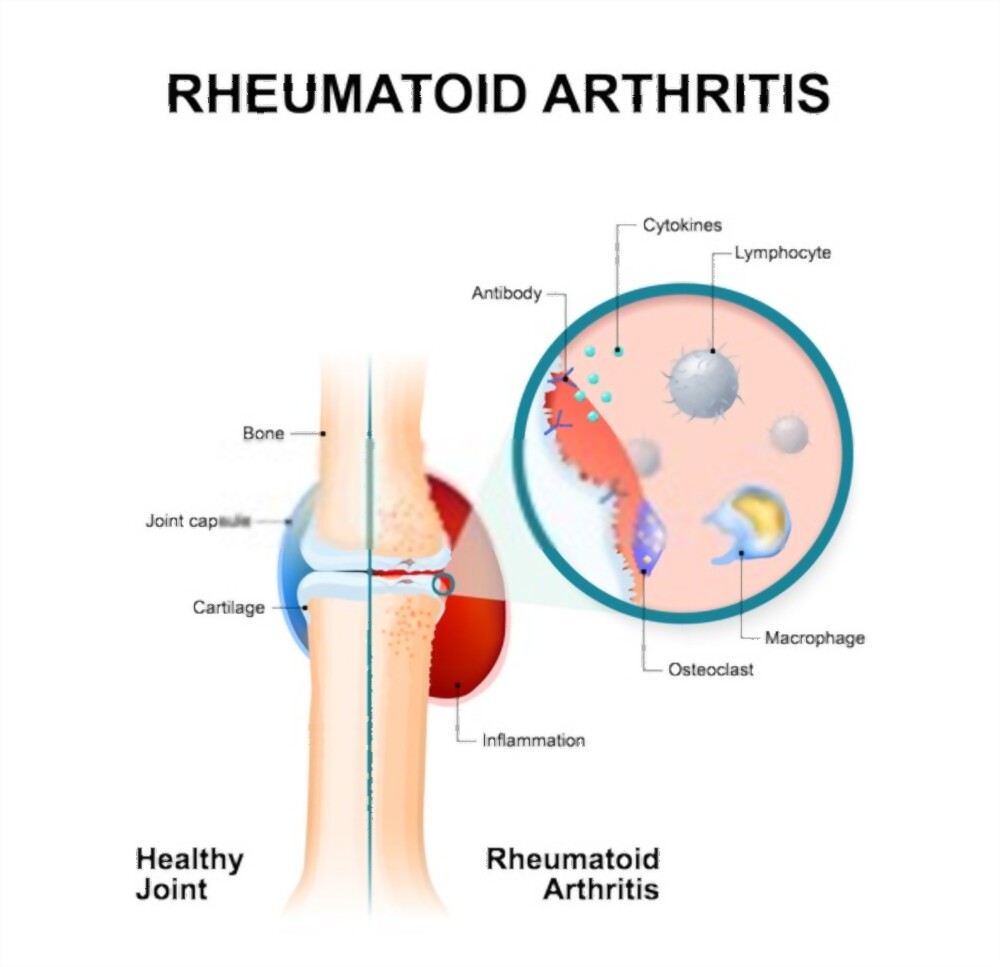
This is an autoimmune disease.
The body’s immune system attacks the joint lining. This causes the lining to be inflamed and swollen. Also, this can eventually harm the bones and the cartilage.
Symptoms
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Redness
- Range of movement decreases
Risk Factor
Gender – Women are more likely to get diagnosed with arthritis than men.
Age – The severity of arthritis increases with age
Recent joint injury – Probability of getting arthritis increases
Obesity – Increase in weight puts a lot of stress on the joints
Diagnostic tests for Arthritis
- X-rays – bone and cartilage damage visible
- Computerized Tomography (CT) – bones and soft tissues visible
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – Soft tissues clearly visible
- Ultrasound (US) – Soft tissue, cartilage and fluid imaging
Treatment for Arthritis

1. Medication
a) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – They reduce pain and inflammation. They have side effects on the stomach and do have risks to the heart. Creams and gels can be applied to the joint.
b) Painkillers / Analgesics – They help reduce pain but have no effect on inflammation.
c) Counterirritant – These are creams and ointments which interfere with pain signals from your joint.
d) Disease-modifying anti-rheumatoid drugs (DMARDs) – They specifically are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
e) Biological response modifiers – These are conjointly used along with DMARDs.
f) Corticosteroids – They include immunosuppressants, they also reduce inflammation.
2. Surgery
a) Joint repair – Joint surfaces can be smoothened or re-aligned to reduce pain and improve movements.
b) Joint replacement – The damaged joint is removed and replaced with an artificial joint. Hip joint and knee joint are most commonly replaced
c) Joint fusion – This is used for smaller joints like the wrist, ankle, fingers, etc.
3. Physiotherapy
Exercise can increase or improve the range of motion occurring at the joint.
Muscles surrounding the joint can be strengthened.
Lifestyle changes for arthritis patients
- Weight loss
- Exercise
- Heat and cold
- Diet containing anti-oxidants
- Avoid fried food, processed food, dairy products, meat
- Gluten free diet
- Acupuncture
- Meditation
- Aquatic exercise
- Yoga
- Massage
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
- Vitamin D
Hot and Cold Therapy
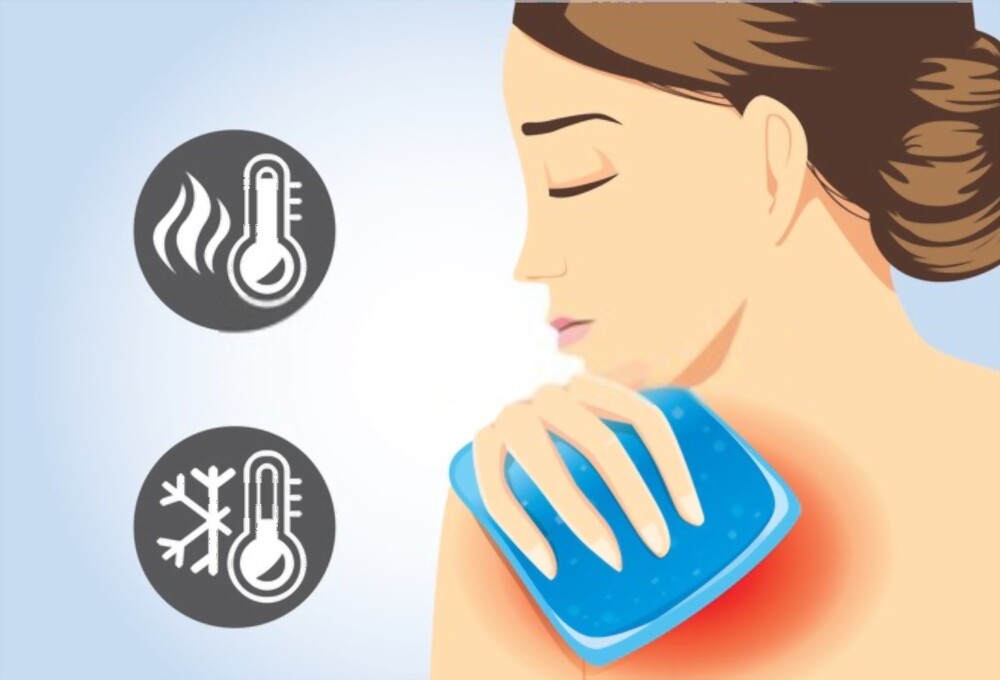
Hot therapy-
- Improves blood circulation
- Increases range of motion
- Warm bath
- Paraffin wax
- Hot packs (water or electric)
- Hot towels
Cold therapy-
- Reduces swelling
- Numbs pain
- Ice towel
- Cold pack
- Ice bag
- Submerging joint in ice water
Also Read: What Are Auto-Immune Diseases? Know Everything About Them – V Cure (vcurehealthcare.com)





