An introduction to IBS-
IBS affects the gastrointestinal system. Presence of abdominal pain and altered bowel habit, with diarrhea, constipation or both constitutes IBS. IBS is diagnosed clinically as there is no biomarker found. It is usually misdiagnosed or poorly understood.
IBS is also known as spastic colon, irritable colon, spastic colitis. It is thus a group of intestinal symtpoms which usually occur together. The symptoms vary in duration and severity in different individuals.
Prevalence and triggers –
- More common in women than men
- Occurs in all age groups ranging from children to elderly. However 50% patients are usually under 35 years of age.
- Familial presence of IBS is associated with higher incidence.
- Anxiety depression and other health issues
- Food products such as wheat, dairy, citrus, beans, cabbage, milk, carbonated drinks.
Symptoms of IBS
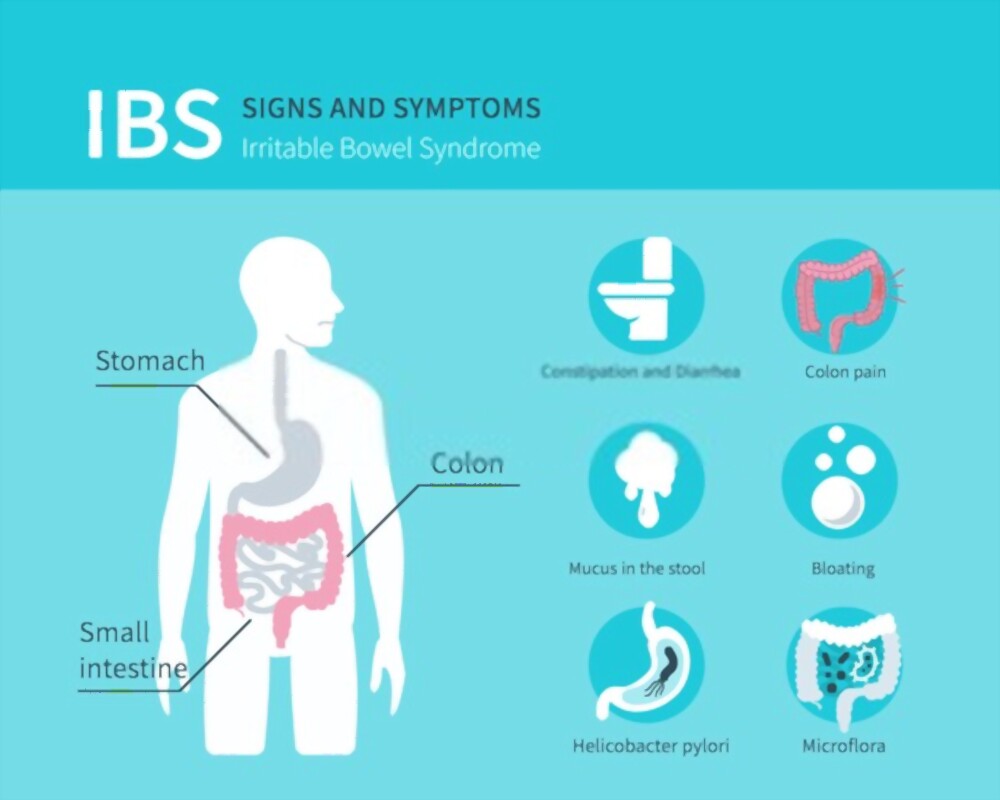
- Abdominal pain or bloating associated with bowel movement
- Appearance changes In bowel movements
- Changes in frequency of bowel movements
- Bloating
- Increased gas
- Presence of mucus in stools
Symptoms usually fluctuate over time. Over short periods of time, some patients may experience resolution of symptoms. However others develop new ones.
Post diagnosis, within 3 months, patients experience four distinct episodes of symptoms per month on average. The longest of these episodes lasts around 5 days. Also, most patients may experience symptoms on more than half of the days.
45% patients subsequently experience other functional gastrointestinal symptoms. Also, Up to two-thirds of IBS patients experience functional dyspepsia.
Moreover, People with higher levels of anxiety are more likely to suffer with other functional comorbid conditions.
Co existing functional conditions –
About half patients show co existing and overlapping symptoms which may be as follows.
- Fibromyalgia
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Back pain, chronic in nature
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Headache
- Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
- Chronic constipation or diaarhea may also cause hemorrhoids.
- Mood disorders.
Causes of IBS –
Factors which play a role are as follows
1. Muscle contractions – stronger and long lasting contractions lead to gas, bloating, diarrhea. Whereas weak intestinal contractions cause hard dry stools as they cause slow food passage.
2. Nervous system -signals occurring between the brain and intestines, if poorly co ordinated causes your body to over react to normal digestive process.
3. Infections
4. Stress
5. Changes in gut microbiome.
Treatment –
Treatment is usually directed towards lifestyle changes. IBS cannot be completely cured, however with treatment, symptoms can be managed effectively.
- Foods to avoid
- Dairy products
- Fried food
- Indigestible sugars
- Beans
Foods which may help reduce symptoms- adding ginger cardamom or peppermint.
When is it important to see a doctor?
If the following symptoms persist, it may be indicative of a more serious problem.
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea at night
- Rectal bleeding
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Unexplained vomiting
- Difficulty swallowing
- Persistent pain. This usually isn’t relieved with bowel movements.
https://vcurehealthcare.com/follow-these-yoga-aasana-for-better-hair-health/Also read –