Introduction to orthostatic hypotension-
The sudden drop in blood pressure on standing from a sitting or supine position refers to as orthostatic hypotension or also as postural hypotension. The blood pressure might drop by as much as or greater than 20mmHg systolically and 10mmHg diastolically. This occurs within three minutes of standing after lying for 5 minutes. This sudden drop in blood pressure is due to variety of reasons which include failure of autonomic reflex, volume depletion, or adverse reaction to medication. However, sometimes patients are asymptomatic.
Causes of orthostatic hyotension –
Orthostatic hypotension occurs in a variety of conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Diabetic nerve damage, Lewy body disease, Vasovagal syncope, Postprandial hypotension, etc. It can also be medication related such as vasodilators, diuretics, anti depressants and anti psychotics.
What signs and symptoms are seen during an episode of orthostatic hypotension?
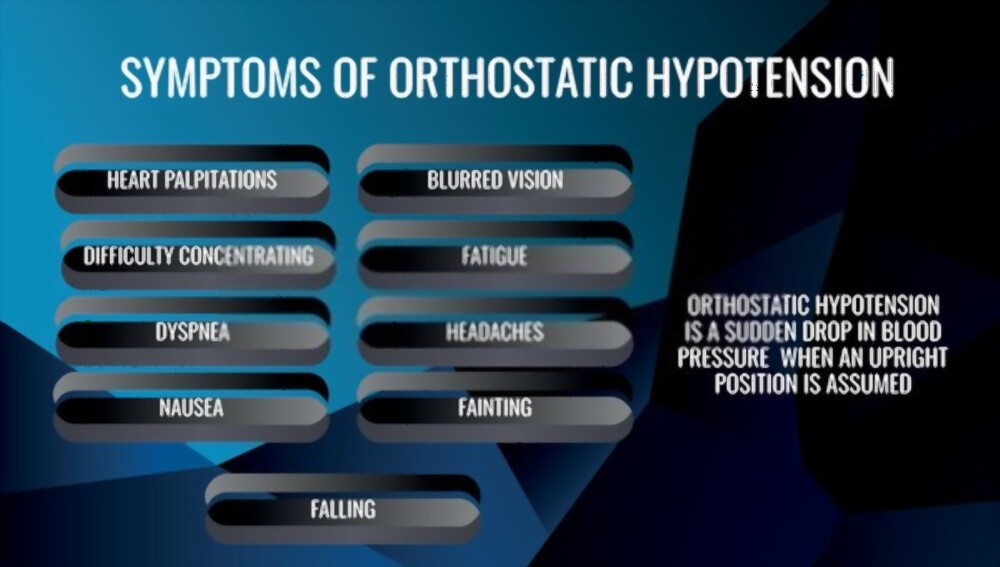
Due to reduced cerebral blood flow occurring as a result of rapid change in position, symptoms such as lightheadedness; generalised tiredness; vertigo; blurred vision; difficulty concentrating; palpitations; anxiety; nausea; and also falls are commonly seen.
Pathology
The pooling of approximately 300 mL to 800 mL of blood in the lower extremities secondary to gravitational forces occur immediately upon standing from a supine position. This causes reduced venous return to the heart, therefore a decrease in cardiac output.
The human body normally compensates with an increase in sympathetic tone and a decrease in vagal tone. This thus refers to as the baroreceptor reflex. This increases peripheral vascular resistance, which subsequently increases venous return and cardiac output, thereby limiting the fall in blood pressure. When patients lack this compensatory mechanism, they present with symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
Diagnosis
Blood pressure is recorded at the following timepoints-
- 5 minutes after lying in a supine position
- 1 minute after standing from a supine position
- 3 minutes after standing
A drop in systolic BP of 20mmHg or greater or drop in diastolic BP of 10mmHg may be seen in people with orthostatic hypotension and is diagnostic.
Lifestyle changes to be incorporated-
- Drink 2-3 litres of water daily
- increasing salt intake
- elevating bed head at night (this helps to decrease fluid to kidneys with resultant urine production)
- use of compression stockings when out
- avoid standing for prolonged periods
- do not go out in hot environment
- do not change posture very rapidly
- eat frequent small meals
- exercising
Exercise guide-
exercises should be performed which help to increase venous return on standing. Some examples of exercises are-
- calf pumps
- static quads
- gluteals static
- static hams
Also read- https://vcurehealthcare.com/ovarian-cancer-types-causes-risk-factors-and-more/





