What is menopause?
The ovarian follicular depletion of a female’s ovaries and loss of ovarian follicular activity refers to a physiological state called as menopause. There is permanent cessation of a womans menstrual cycle. Menopause marks the end of reproductive years.
The average age is usually above 50 years.
Menopause is associated with physical, psychological and social effects.
Types of Menopause-
Physiological –
The natural spontaneous progressive decline of the menstrual cycle refers to physiological menopause. It occurs due to natural decline of the ovarian function.
Pathological –
Premature menopause occurs when there is cessation of periods before the age of 40.
Surgical menopause: this occurs due to surgical intervention, or chemotherapy.
Delayed menopause: cessation of periods after the age of 55.
Symptoms-
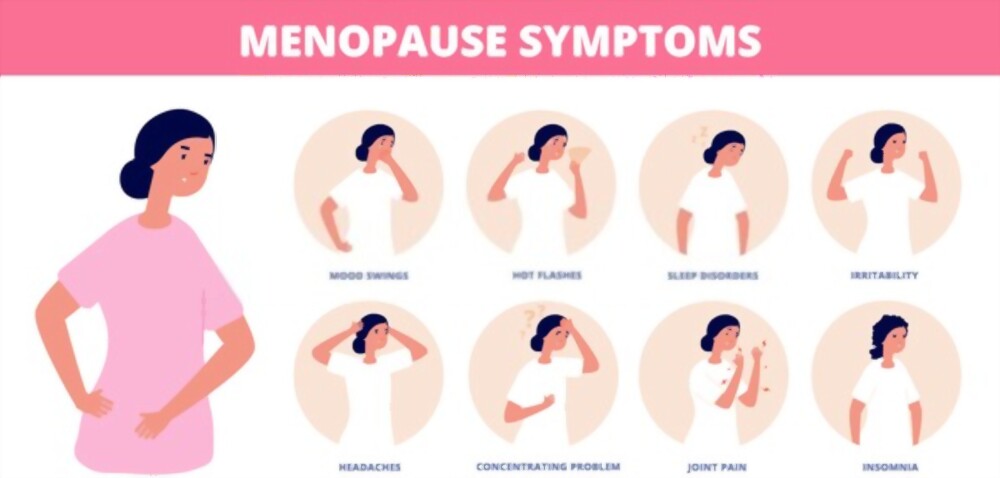
- Hot flushes- This refers to a sudden sensation of heat along with perspiration.
- Vaginal dryness
- Depression
- Sleep disturbances
- Joint pain
- Uneven or missed menstrual cycles
- Sore breasts
- Emotional changes
- Changes in libido
- Muscular pain and fatigue
Stages-
Perimenopause. When the production of estrogen by the ovaries gradually begins to decline. This may last upto 1-2 years until the time ovaries do not produce eggs.
Menopause– This marks the end of egg production by the ovaries and the cessation of menstrual cycle.
Postmenopause- The years after menopause are referred to as post menopausal phase. It is associated with increased health risks due to hormonal changes.
Long term consequences-
- Bone loss-due to estrogen deficiency. There is loss of cortical and trabecular bone loss.
- Cardiovascular diseases- there is a risk of cardiovascular diseases in post menopausal women due to changes in lipid function.
- Osteoporosis– occurs due to reduction in bone density
- Weight gain and obesity
- Risk of alzheimers
- Weaker vision
Exercising and menopause-
- Weight-bearing exercise: these include low impact exercise forms such as ypga and walking, along with high impact exercises such as jogging.
2. Strength Training Exercise- These include weight lifting, swimming, cycling.
Physical exercise reduce the risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease depression and obesity.
Beneficial foods and diet-
- Vitamin D- it is important for maintaining bone density.
Recommendation For adults- 5 μg/day (19–50 years)
10 μg/day (51–70 years)
15 μg/day (>70 years).
2. Omega 3 fatty acids- these are essential for their anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and insulin-sensitizing effects.
3. Vitamins
4. Probiotics
Lifestyle changes to be incorporated-
- Use a lubricant for dryness.
- Exercise regularly to sleep better
- Strengthen your pelvic floor muscles with Kegel exercises
- Stay socially and mentally active
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Maintain a nutritious diet
- Practice deep breathing to help you relax.
Also read- https://vcurehealthcare.com/understanding-the-risk-population-for-iron-deficiency/





