Background-
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common condition. It causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and sometimes also in the arm. It occurs when the median nerve is compressed as it travels through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. About 4-5% people worldwide suffer from CTS, women more common than men. The susceptible age group for occurrence of CTS is 40-60 years. It is a disorder caused due to repetitive wrist activity.
Risk factors for CTS-
- Obesity
- Monotonous and repetitive wrist activity- Excess and repetitive wrist flexion and extension
- Exposure to vibration
- Pregnancy
- Genetic heredity
- Menopause
- Kidney failure
- Hypothyroidism
- Use of oral contraceptives
- Diabetes
Symptoms-
- Pain in the hand
- Numbness
- Tingling.
- Reduction in grip strength
- Reduced hand function
- Muscle wasting in later stages
Area involved- thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the radial side of the ring finger.
The pathophysiology of CTS-
A combination of mechanical trauma, increased pressure, and ischemic damage to the median nerve within the carpal tunnel lead to CTS. The repetitive change in the position of the wrist may result in dramatic shifts in the fluid pressure. As such, the extension increases the pressure to more than 10 times. Flexion causes an eight times increase in the pressure. With continuous compression, blood flow is interrupted, causing ischemia, and thus local metabolic alterations.
Stages of CTS
In the first stage- numbness or swelling is present on the hand, with no noticeable swelling. The patient may also feel extreme pain which ceases after shaking the hand.
The second stage of CTS- symptoms occur when the patient engages in a repetitive activity involving the hand or wrist. Symptoms may also occur if they maintain a specific position for extended periods. Presence of clumsiness when using hands to grip objects is also noted.
The final stage involves hypotrophy or atrophy of the muscles.
Treatment options
In minor and moderate cases- conventional treatment which includes splinting, corticosteroids, physical therapy, therapeutic ultrasound.
For severe cases, however a surgical decompression is required.
Occupations associated with an increased risk of CTS-
- Electronic assembly workers
- Quarry drillers
- Automobile workers
- Dentists
- Surgeons
- Jobs involving use of vibratory tools
- Desktop users with frequent mouse use and typing
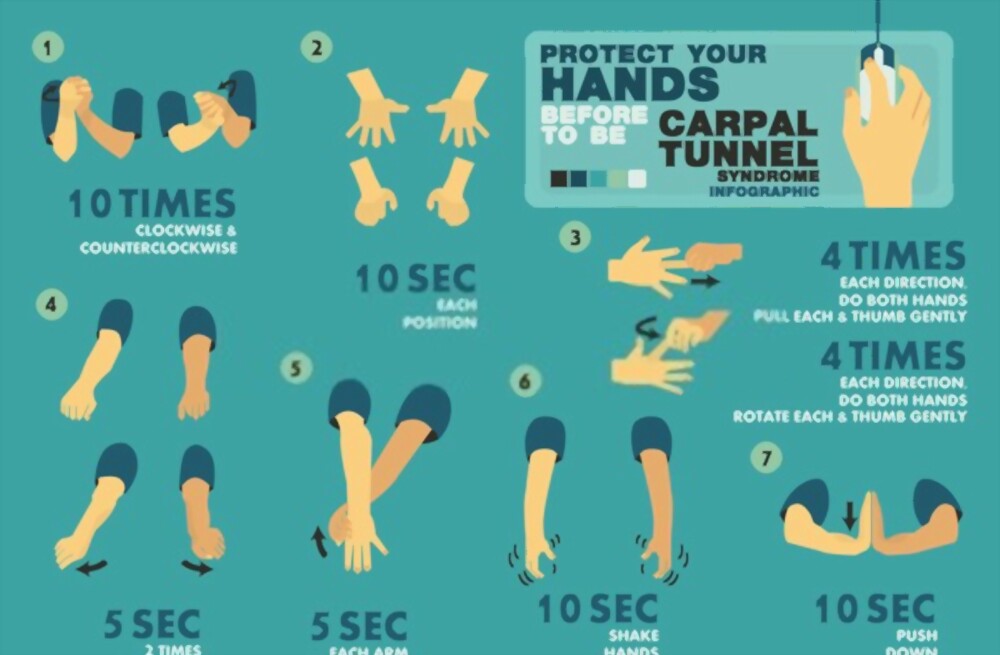
Exercise to maintain your wrist in correct posture-
Also read – https://vcurehealthcare.com/rheumatoid-arthritis-an-overview/





