Because Vitamin E is essential for your body to function properly, it is necessary. It’s fat-soluble, which means it needs fat from the diet to absorb correctly. Before being released into the bloodstream, vitamin E is primarily stored in the liver.
Deficiency is uncommon and usually occurs as a result of another ailment. Low amounts can also be found in preterm babies.

There are eight chemical variants of vitamin E. A doctor can determine how much of one form, alpha-tocopherolTrusted Source, a person has used a blood test. They can use this information to establish whether a person’s overall vitamin E level is adequate.
What is the significance of vitamin E?
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant vitamin that aids in the maintenance of a healthy immune system. It is naturally found in a variety of foods and is added to certain foods to help you gain more from it.
As a result, unless you have an underlying health problem, getting a vitamin E deficit is uncommon. Vitamin E in high concentrations can cause an increase in blood pressure.
How much vitamin E are you supposed to take?
Vitamin E needs to be 15 milligrams (mg) per day for adults and children 14 years and older.
Children under the age of six require a lower daily dose:
– aged 1 to 3: 6 mg per day
-aged 4 to 8: 7 mg/day -children aged 9 to 13: 11 mg/day
Breastfeeding mothers should take 19 mg each day.
You can meet your vitamin E requirements by combining a few items each day. Consider the following scenario:
Sunflower seeds have 7.4 mg of vitamin E per ounce.
The vitamin E content of two tablespoons of peanut butter is 2.9 milligrams.
In 1.9 milligrams per half spinach cup.
Vitamin E insufficiency symptoms
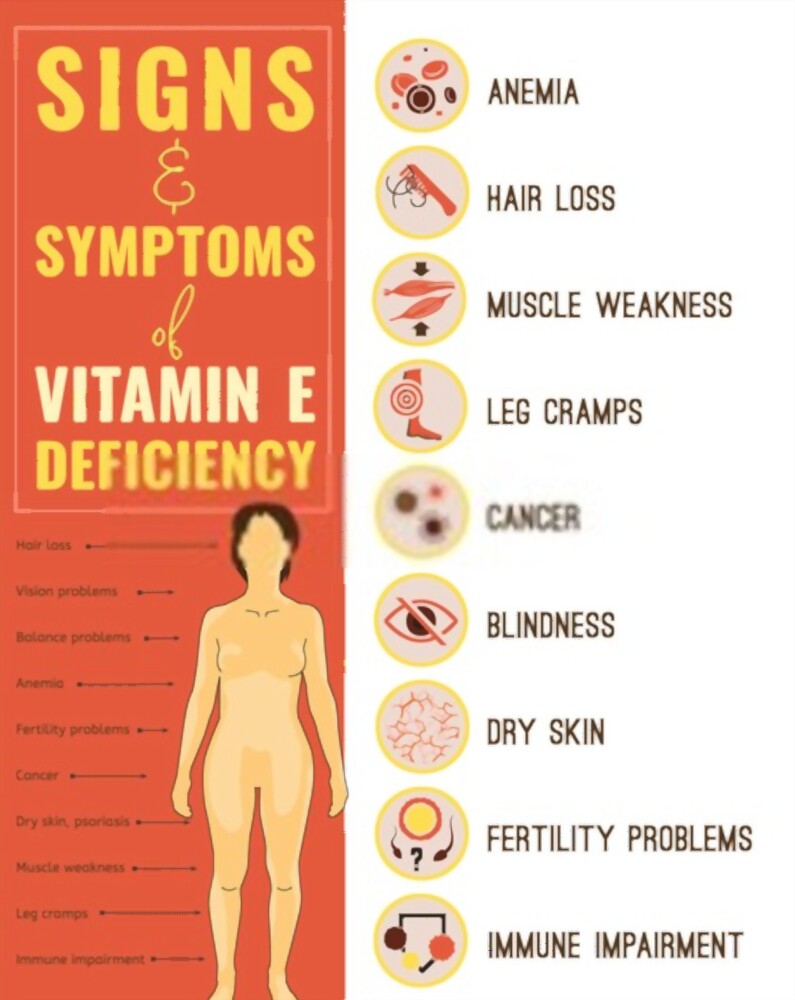
Vitamin E insufficiency is quite uncommon. However, the following symptoms could indicate that it is happening to you:
Muscle aches and pains
The central nervous system relies heavily on vitamin E. A deficit can harm nerves and muscles, resulting in muscular weakness or discomfort.
Numbness and tingling sensations
Nerve and muscle injury can result in a lack of sensation, particularly in the arms and legs.
Walking and coordination issues.
Coordination can be difficult due to nerve and muscle injury. Walking, for example, can become more difficult as a result of this.
Issues with vision
Those who do not receive therapy for severe vitamin E deficiency may lose their vision over time.
Immune system deficiency.
The deficiency of vitamin E can lead to inhibition of immune cells.
According to studies, due to changes in the immune system that occur as we age, older persons have a higher demand for vitamin E.
Vitamin E deficiency causes
-Genetics
Insufficiency of vitamin E is often an inheritance. Learning about your family’s medical history can help you diagnose certain rare, inherited disorders. Congenital abetalipoproteinemia and familial isolated vitamin E insufficiency are two of these disorders that are persistent and cause severely low vitamin E levels.
-Medical problems
Vitamin E insufficiency can also occur as a result of disorders that severely limit fat absorption. This is due to the fact that the body requires fat to properly absorb vitamin E.
The following are a few of these ailments:
-celiac illness -chronic pancreatitis
-liver cholestatic disease
Cystic fibrosis is a trusted source.
In newborns and babies born prematurely, who have lower birth weights and less fat, deficiency is also common.
Because an undeveloped digestive tract might interfere with fat and vitamin E absorption, premature newborns are especially vulnerable.
The deficiency of Vitamin E in young babies can cause hemolytic anemia, which causes red blood cells to die.
Vitamin E insufficiency is the result of a number of diseases.
The deficiency of vitamin E is often a result of a medical condition.
You should be on the alert for this insufficiency if you have one of these disorders. If you observe signs of vitamin E deficiency and don’t have a diagnosis, you should see a doctor.
-Crohn’s illness
-chronic pancreatitis
-cholestasis
-cystic fibrosis
-primary biliary cirrhosis
-celiac disease
-short bowel syndrome
-ataxia caused by a lack of vitamin E
Deficiency is very common in newborn and premature babies with low birth weights and fat levels.
Complications
A person should not take too many fat-soluble vitamin supplements, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Vitamin E overdose can result in irregular bleeding, muscle pains, diarrhea, and vomiting. The bleeding can increase your chances of having a stroke and dying young.
Blood thinners, such as warfarin, and chemotherapy drugs might be affected by too much vitamin E.
All supplements and vitamins taken on a daily basis should be disclosed to the doctor. Unless directed otherwise by a physician, do not exceed the prescribed supplement dosage.
When should you see a doctor?
If you have no family history of the genetic disease but are experiencing any of the symptoms of vitamin E insufficiency, you should see a doctor.
A dangerously low quantity of vitamin E in the blood can signal a serious health problem. Additional tests will aid in the identification of the cause and therapy choices.
Supplementation
Although taking supplements is a common approach to add vitamins and minerals to your diet, taking vitamin E in supplement form should be avoided.
Because the US Food and Drug Administration does not regulate supplements, it may be challenging to determine the quality of the contents.
Even if you buy a supplement from a trustworthy company, it’s possible that it will interact with other prescriptions you’re on.
The following are some of the drugs that may be affected:
-anticoagulants
-antiplatelets
-simvastatin
-niacin
-chemotherapy medicines -anticoagulants
-antiplatelets
-simvastatin
-niacin
-anticoagulants
-antiplatelets
-anti
-drugs used in radiotherapy
Because they aren’t regulated, it’s possible that you won’t know how much vitamin E you’re getting. Some supplements, for example, only contain one kind of vitamin E. Other types, which can be found in a variety of foods, are required by your body. Whole foods, rather than supplements, are the best source of nutrients.
It’s possible that concentrated supplements, rather than multivitamins, contain more vitamin E than you require. This could have negative consequences and lead to more issues.
What therapy alternatives are available?

Supplementing with vitamin E is frequently beneficial.
Premature infants and newborns
Vitamin E supplementation is currently administered via a tube inserted into the stomach. It can also be given intravenously when necessary.
While one dose may be enough to enhance vitamin E levels in the blood, numerous doses may be required.
Adults and children
Supplementation is required for children and adults with deficiencies caused by hereditary disorders.
Vitamin E in strong amounts from a reliable source.
Supplementation can halt the disease’s course. When a deficiency is discovered early on, it may be possible to avoid neurological effects.
Is there such a thing as too much vitamin E?
Yep.
There is no such thing as too much vitamin E. (or an excess of any fat-soluble vitamin, for that matter).
Too much vitamin E in the form of supplements might cause irregular bleeding. This bleeding may increase your chances of having a stroke or dying young.
In two clinical trials, people who took vitamin E supplements had a higher risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Vitamin E intake has also been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer in healthy males, according to research.
Researchers have yet to discover if consuming vitamin E-rich foods has any detrimental consequences.
Dietary sources of vitamin E

Unless a person has an underlying chronic disease, a hereditary condition, or a diet that is exceptionally low in fat, it is exceedingly unusual that they have low vitamin E levels. Supplementation is rarely essential for others.
A wide range of foods may contain vitamin E. Because the body is unable to generate it, it must be received from diet or supplementation.
Following foods contains Vitamin E :
-vegetable oils such as wheat germ oil, peanut oil, and extra virgin olive oil
-seeds and nuts
-complete grains
-milk -spinach, Swiss chard, red peppers, and avocados, to name a few
Vitamin E has anti-aging properties.

Using vitamin E oil on your face can benefit you in a variety of ways.
Remember that the evidence for these advantages varies, and some of it is essentially anecdotal.
Pigmentation of the skin
Hormones or other factors induces too much pigment (melanin), which can cause dark patches on your skin. Melasma is an allegedly curable skin disorder with topical vitamin E.
Preventing wrinkles and ageing on the face
Vitamin E is abundant in antioxidants and also has a calming effect on the circulatory system. Thus, that could explain why some detect a difference in their skin’s firmness and structure after applying vitamin E oil topically.
Acne scar treatment
Some people swear by vitamin E as an acne scar cure. While vitamin E appears to improve circulation, it does not appear to hasten the healing process. As a result, using it to treat acne scars may not produce the desired benefits.
For silky, supple lips
Topical vitamin E oil can help relieve chapped, dry lips. Because vitamin E increases cell turnover and regeneration, it helps to bring new cells to the surface of dry lips more quickly.
Vitamin E oil’s thick, greasy viscosity can also help to avoid further discomfort.
Takeaway
When an adult has a vitamin E deficit, it is most commonly due to a persistent sickness or a genetic issue.
For therapy, you should seek a professional and certified nutritionist with experience with the disease.
When a low-fat diet is the cause of the shortage, it can be corrected by adding fats to the diet.
However, to stop the progression of the sickness and avoid complications, vitamin E supplementation will be required on an ongoing basis. The forecast is normally good if an individual is diagnosed early and continues to be treated.
Vitamin E supplementation, toxicity, and safe limitations are still being studied.





