Women may seek help from medical personnel for many conditions, such as pelvic health. In this article, lets explore some common conditions that women encounter in their daily lives.
Pelvic Floor States
Underactive
Overactive
There are two types of pelvic floor states.
1. Underactive Pelvic Floor
- Low in position, unsupportive, hypotonic in nature.
- Is unable to provide pelvic organ support due to deficits in power or endurance .
2. Overactive Pelvic Floor
- High in position, tight, short, hypertonic in nature.
- Is unable to fully relax and lengthen.
Some women may experience symptoms of both overactivity and underactivity. This refers to a mixed pelvic floor.
Common conditions are discussed below.
1. Incontinence
Urinary
Faecal
Incontinence is the uncontrolled loss of urine, gas, or stool.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI) can be categorised as:
- Stress incontinence
- Any activity which increases intra abdominal pressure causes involuntary loss of urine. These movements / activities can be coughing, sneezing, laughing, running, heavy lifting.
- Urge UI:
- An unintentional loss of urine that can occurs with contraction of bladder.
- There is a sense of urgency.
- Mixed UI:
- An individual has both a combination of stress and urge UI
- Overflow incontinence:
- UI occurs when the bladder is full excessively, without any attributed cause.
- Functional incontinence:
- Occurs when there are cognitive, functional, or mobility issues.
There are no bladder or neurological causes identified.
Faecal Incontinence
Faecal incontinence is an involuntary loss of gas or stool. This is expererienced by One in eight women. The main cause is identified as obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIS) that occur during childbirth.
2. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
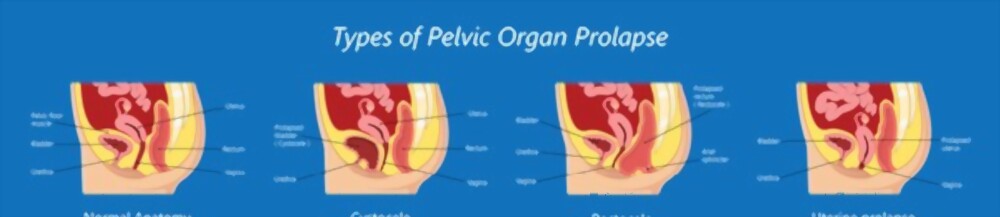
Prolapse is a condition when any of the pelvic organs which could be the uterus, rectum and bladder in women move from their optimal anatomical position.
Symptoms
- A feeling of pressure in the perineum
- Altered urine output
- A feeling of falling out
- Constipation / straining
- Discomfort during intercourse
- Bulge sensation
- A feeling of pressure
- Bladder storage symptoms
- Urinary incontinence
- Recurrent UTIs
Causes of prolapse
- weak pelvic floor muscles are compromised
- myofascial tension in the deep and superficial layers of the muscles.
- Lax ligaments
- less support to pelvic structures
Types of Prolapse
Types of prolapse include
- Rectocele (prolapsed rectum)
- Uterine prolapse (prolapsed uterus)
- Urethrocele (prolapsed urethra)
- Enterocele (prolapsed intestine)
- Vaginal vault prolapse (top of the vagina prolapses – only occurs after a hysterectomy)
- Cystocele (prolapsed bladder)
3. Persistent Pelvic Pain
Pain lasting more than 3 months around pelvic area is called Persistent pelvic pain is
Sites include
lower abdomen, hips, groin, low back, coccyx, perineal region, rectum, genitalia, etc
Types of pain commonly experienced by women
- Dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
- Coccydynia (coccyx pain)
- Dysmenorrhea (painful periods)
- Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (a descriptive diagnosis)
- Pelvic girdle pain
- SI joint pain
4. Vaginal health in pregnancy
Increased vaginal discharge
An increase in vaginal discharge is caused by high levels of estrogen and progesterone. An increase in blood volume and blood flow also causes increased discharge.
Pregnancy discharge should be thin, white,without an odd odour.
Increased risk of vaginal infections
Vaginal infections commonly occur during pregnancy
Yeast infections:
Symtoms
Itching in Vagina
cottage cheese discharge
vaginal burning.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV):
This produces a fishy-smelling, gray discharge. More common with pre-term labor, low birth weight, and miscarriage.
Increased vaginal swelling
There is increase in blood flow To support your growing baby. This causes vagina to appear swollen and feel fuller.
In some cases, vaginal swelling may be caused by infection. If vaginal swelling is accompanied by redness, burning, and itching, it could highly be indicative of an infection.
Vaginal bleeding
- Bleeding may occur during first trimester. It may be due to the implantation of the fertilized egg to the uterus lining. It may also be caused by increased blood volume. In some cases bleeding is a sign of miscarriage.
Vaginal bleeding during your second and third trimesters, needs to be consulted.
Causes-
Vaginal health after giving birth
Vaginal bleeding – Bleeding is common for two to six weeks after giving birth.
Kegel exercises performed during and after pregnancy help increase vaginal tone. They improvemuscle strength and prevent prolapse.
Also read- https://vcurehealthcare.com/understanding-anxiety-and-how-to-deal-with-it/





