Introduction to ovarian cancer-
Ovarian cancer (OC) is one of the most common gynecologic cancers associated with a high mortality rate.
It includes several types of cancer that all arise from the cells of the ovaries.
Types- (3 types)
- Epithelial – derived from the cells on the surface of the ovary or fallopian tube. (most common, 70% cases)
2. Germ cell – derived from egg producing cells
3. Cord-stromal cell – derived from the ovarian connective tissue
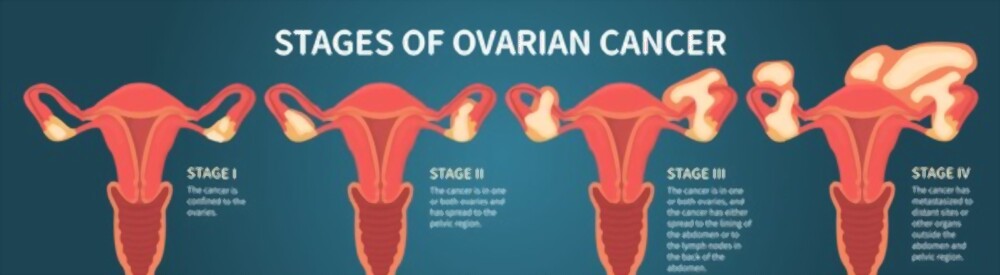
Stages-
- I – cancer limited to the ovary.
- II – cancer involves pelvic extension along with ovaries.
- III – Growth of the cancer involves one or both ovaries, along with either extension beyond the pelvis to the lining of the abdomen or upto the lymph nodes.
- IV– most advanced stage, with metastases outside peritoneal cavity.
Population at risk for developing ovarian cancer–
- nulliparity
- age >50
- early menopause
- family history
- BRCA1/BRCA2
- Lynch syndrome
- smoking
- previous history of cancer
Clinical presentation seen-
- Bloating.
- Vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Pain in the pelvic or abdominal area
- Abdominal distension or discomfort
- Abdominal mass
- Back pain
- Painful urinination or frequent urges
- Constipation, or diarrhea
- Weight Loss
- Persistent lack of energy
Causes of cancer-
ovarian cancer begins when cells in the ovaries develop DNA mutations. Thus the cells tend to grow and multiply quickly, creating a mass (tumor) of cancer cells, which continue living when healthy cells would die. They can invade nearby tissues and also break off from an initial tumor to spread to other parts of the body. This thus refers to as metastasis.
Prevention-
- Discuss your risk factors with your doctor. If you have a family history of breast and ovarian cancers, or moreover If you’re found to have a gene change that increases your risk of ovarian cancer, it is important that you discuss it with your doctor.
Treatment options–
Surgery, chemotherapy, and also radiation.
- Surgery. Depending on the spread of cancer, the ovaries, uterus, cervix, or fallopian tubes may need to be removed. Also, Other tissue typically removed includes lymph nodes, and all visible cancer.
2. chemotherapy drugs
3. radiation therapy – Radiation is used for treating cancer recurrence. It is also used to manage pain symptoms.
4. Targeted Therapy. Targeted treatments find and attack cancer cells while doing little damage to surrounding normal cells.
5. Hormone Therapy- use of hormone or hormone blocking medications to treat cancer.
Conclusion-
Considering the impact of ovarian cancer on women’s health, preventive measures, health education, early detection in high risk groups are therefore highly recommended.
Did you know?
Ovarian cancer is the fifth most common cause of death from cancer in women.
Also read- https://vcurehealthcare.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-cupping-therapy/





