Diabetes is a long-term health condition that impacts millions of people around the world. It occurs when the body struggles to regulate blood sugar levels properly, leading to potential health complications if left unmanaged. It occurs when the body struggles to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels properly. There are two primary types—Type 1 and Type 2—each with different causes, risk factors, and treatment approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial for managing the condition effectively and maintaining good health.
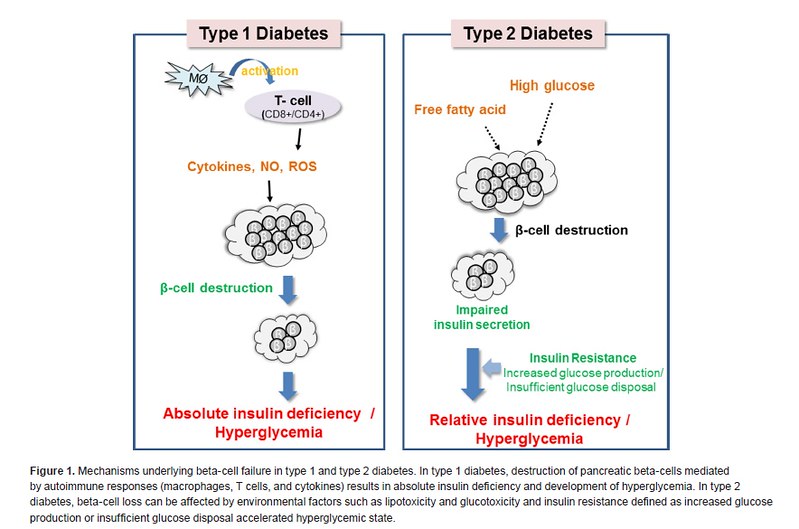
What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
An autoimmune condition known as type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system unintentionally targets the pancreatic cells that produce insulin. By permitting glucose to enter cells for energy, the hormone insulin aids in blood sugar regulation. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to dangerously high blood sugar levels.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Since insulin is essential for helping glucose enter cells and provide energy, this leads to high blood sugar levels and the need for lifelong insulin therapy. Unlike Type 2 diabetes, Type 1 is not linked to lifestyle factors such as diet or obesity.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop rapidly and may include:
• Excessive thirst
• Frequent urination
• Unexplained weight loss
• Fatigue and weakness
• Blurred vision
• Extreme hunger
• Irritability or mood changes
Since Type 1 diabetes is often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, it is sometimes referred to as “juvenile diabetes.” However, adults can also develop this condition.
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes
While Type 1 diabetes doesn’t have a cure, it can be effectively managed through:
• Insulin therapy – Since the body no longer produces insulin, daily insulin injections or an insulin pump are required.
• Blood sugar monitoring – Regular glucose checks help prevent complications.
• Healthy diet and exercise – While not a cure, balanced nutrition and physical activity can help keep blood sugar levels stable.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body either becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it. This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause long-term damage to organs and tissues if left uncontrolled. Unlike Type 1, Type 2 diabetes develops gradually and is more common in adults, although it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger people due to rising obesity rates.
Causes and Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is brought on by a number of causes, such as:
• Obesity – Carrying excess weight, particularly around the abdominal area, can lead to increased insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to effectively use insulin.
• Sedentary lifestyle – Lack of physical activity contributes to poor glucose regulation.
• Unhealthy diet – Diets high in sugar and processed foods raise the risk.
• Genetics – If there is a family history of diabetes, the risk of developing the condition is higher, as genetic factors can play a role in its development.
• Age – The likelihood of developing Type 2 increases as you get older, especially after the age of 45, due to factors like decreased physical activity and changes in the body’s ability to manage blood sugar.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with Type 2 diabetes may not experience noticeable symptoms at first. However, as the condition progresses, common symptoms include:
• Increased thirst and frequent urination
• Slow-healing wounds
• Fatigue
• Blurred vision
• Numbness in hands/feet can be a sign of nerve damage from diabetes.
• Frequent infections (e.g., skin, gums, or urinary tract)
Treatment and Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which requires insulin from the start, Type 2 can often be managed through lifestyle changes. However, some individuals may need medication or insulin therapy if their condition worsens.
Key management strategies include:
• Healthy eating – A diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and healthy fats helps regulate blood sugar levels.
• Regular exercise – Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps with weight management.
• Weight loss – Losing even a small amount of weight can have a significant impact on blood sugar control.
• Medications – Some people may require oral medications like metformin or, in some cases, insulin.
Key Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
| Feature | Type 1 | Type 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells | Insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production |
| Onset Age | Usually diagnosed in children or young adults | More typical among adults but becoming more common in younger groups. |
| Insulin Production | Little to no insulin production | Insulin is produced but not used effectively |
| Treatment | Requires insulin injections or pump | Lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes insulin |
| Prevention | Not preventable | Often preventable through a healthy lifestyle |
Prevention and Reducing Risk
While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, Type 2 can often be delayed or avoided by making healthier choices, such as:
• Maintaining a healthy weight
• Following a balanced diet including lean proteins, healthy grains, and veggies calls for vegetables.
• Staying physically active
• Reducing sugar and processed food intake
• Getting regular health checkups to monitor blood sugar levels
Conclusion
Diabetes is a lifelong condition, but it doesn’t have to control your life. Whether it’s Type 1 or Type 2, understanding the disease and taking the right steps can make a huge difference. Type 1 requires insulin and careful monitoring, while Type 2 can often be managed with lifestyle changes. The key is early detection and staying on top of your health. If you or someone you know is at risk, don’t wait—talk to a doctor, make small changes, and take control of your health one step at a time.
Also Read About : Breakthrough in Diabetes Prevention: This Simple Test Could Save Your Child’s Future!
Visit Us At : https://g.co/kgs/rTqAjgt





