What are White Blood Cells?
These are the major cells that provide immunity for our body to fight against infections and diseases. They are produced in the bone marrow. They are present in the blood plasma and lymph all the time. There are 2 main types of granulocytes and agranulocytes.
Granulocytes include neutrophils, acidophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes. All of these types are distinguished by the size and/or shape of their nuclei as well as their physical and functional characteristics.
- Neutrophils – act against bacteria and fungi
- Acidophils – act against allergic reactions
- Basophils – act against inflammatory responses
- Monocytes – destroy harmful microbes and particles
- Lymphocytes – release antibodies, provide autoimmunity
Normal counts
- Neutrophils – 60 to 65%
- Acidophils – 2 to3 %
- Basophils – 0 to 1%
- Lymphocytes – 20-40%
- Monocytes – 4-8%
What is immunity?
Immunity is a system that is capable of recognizing and tolerating what belongs to self and recognizes and destroys what is foreign (new and harmful for the body).
When we say our body is immune to a particular disease, that means, our body is able to recognize the harmful element (collectively called pathogens) and is able to destroy it instantly. Sometimes, even without you getting to know about it. That is how strong the human body is!
All of us are constantly exposed to so many different types of particles. They are present everywhere- in the air, in water, on surfaces, on our hair, etc. They are microscopic and invisible to the naked eye. Yet not all of us fall sick frequently. If this system wouldn’t exist, we all would have fallen sick every day!
Features of the Immune System
- Capability of discriminating between self and non-self (foreign) – immune system reacts against foreign molecules, irrespective of its nature
- Specificity – for each antigen (foreign body) there is a specific lymphocyte
- Memory – produced during the first response. The second response to the same antigen is quicker and more effective
Vaccine is a type of immunity!
The vaccine contains dead or weakened pathogens. When you take any vaccine, your body’s immune system is exposed to that pathogen. The production of WBC increases. A special type of WBCs, called Memory cells, are produced.
These cells remember the particular pathogen. The next time when the same pathogen enters your body, the defense is faster because of the memory cells recognizing the pathogen.
What are Auto-immune diseases?
In immune system disorders, the immune system either shows abnormally low activity or shows overactivity. Low activity causes the body to the susceptible to a huge range of diseases. This is because the body is unable to fight the invaders. Overactivity leads to auto-immune diseases.
Diseases, where white blood cells are not able to differentiate between self and non-self (foreign) particles and end up harming normal healthy cells, are known as autoimmune diseases.
Auto-immune diseases include-
And many more. There are at least 80 types of autoimmune diseases.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
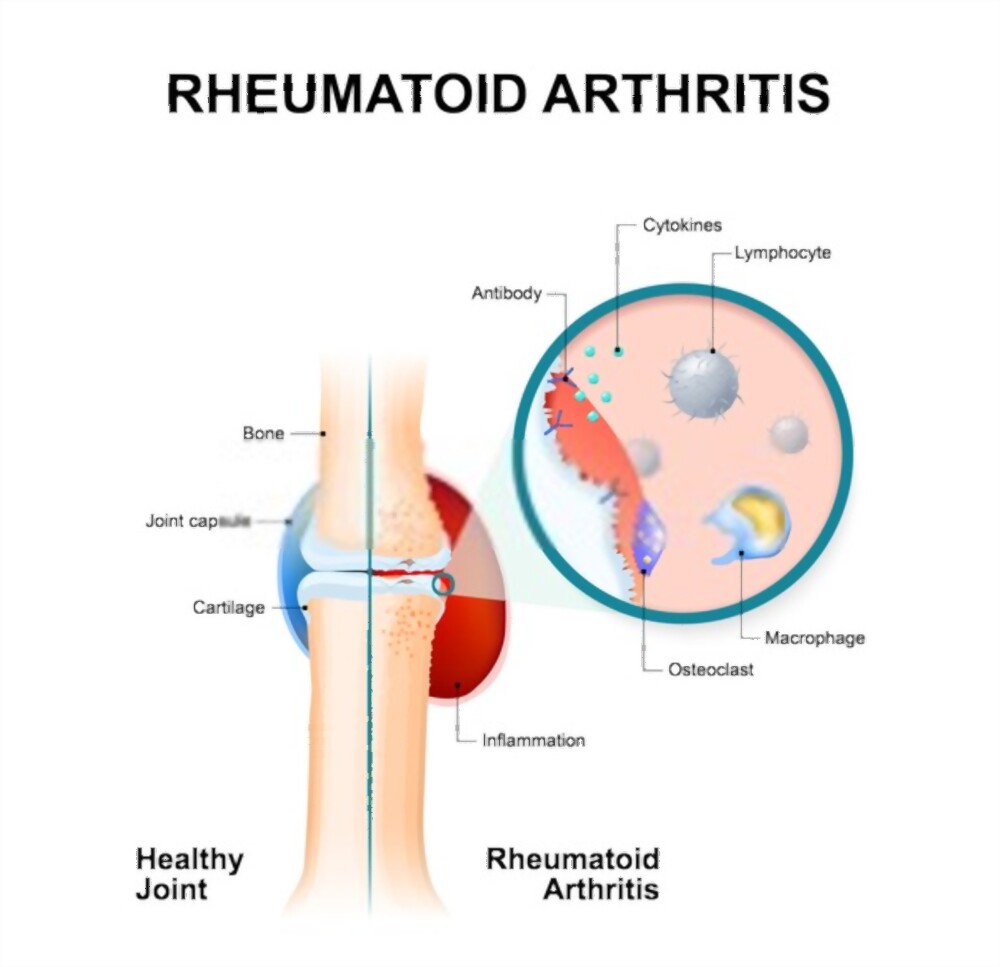
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that can affect joints. In severe conditions, it may also damage skin, eyes, lungs, blood vessels, and other body systems.
The immune system mistakenly attacks your own body tissues.
Antibodies attach to the lining of the joints, causing inflammation, swelling, and pain.
Symptoms-
- Swelling in joints
- Joint stiffness
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Myasthenia Gravis
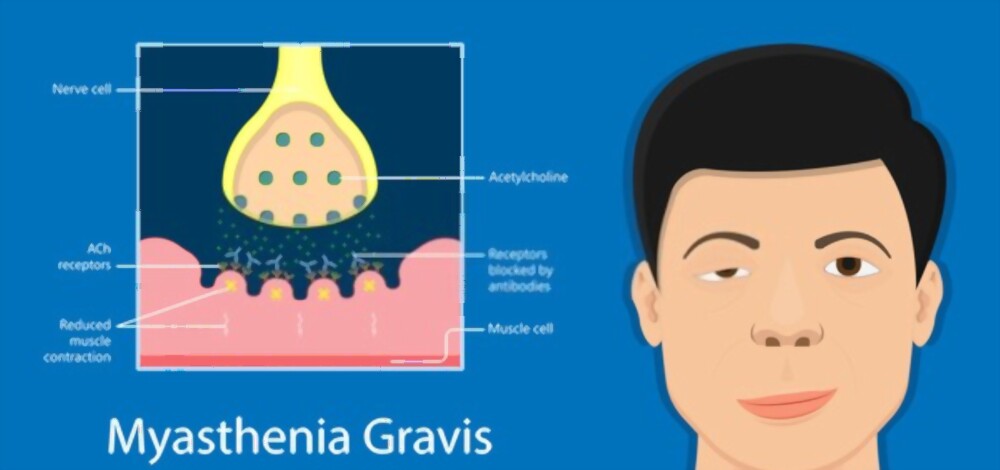
It is a neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness in skeletal muscles (muscles used for bodily movements). Communication between nerve cells and muscle cells weakens.
Antibodies bind to the nerves.
Symptoms-
- Fatigue
- Difficulty in breathing
- Drooping of eyelids
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Double vision
- Problems walking up the stairs
- Problems lifting objects
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
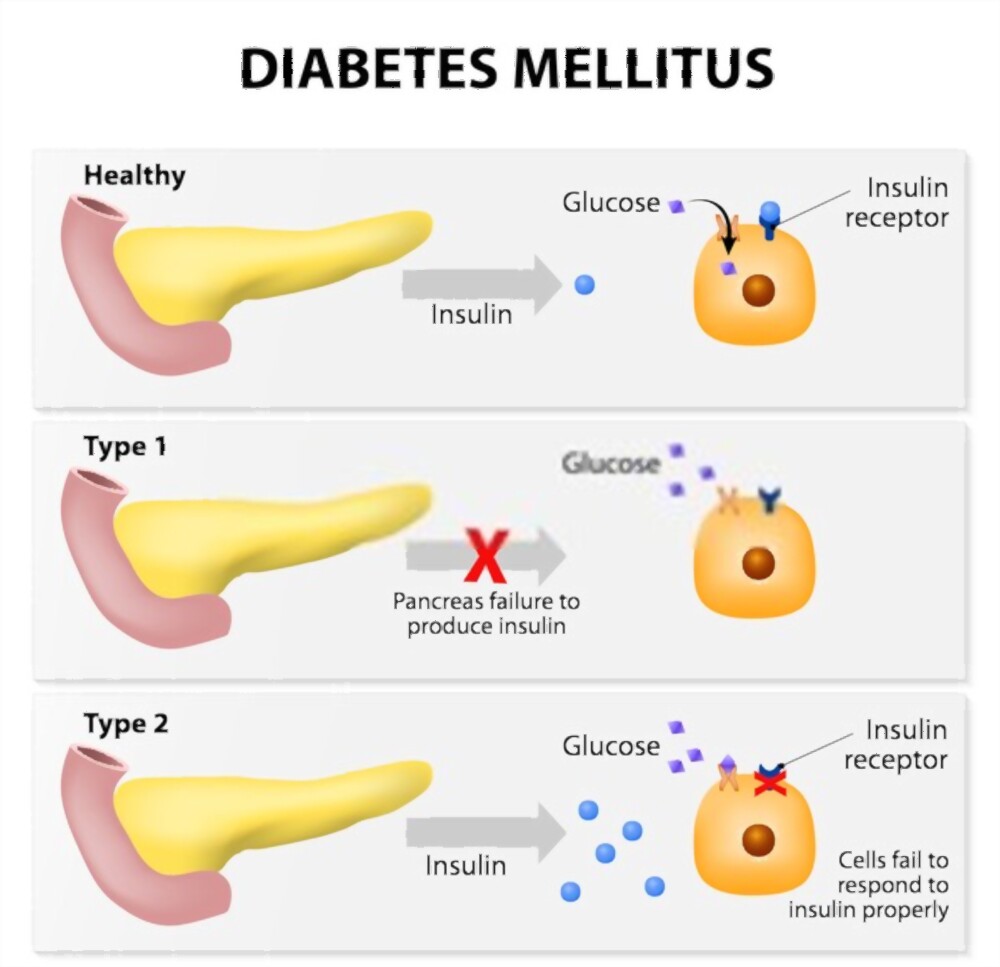
Here, the immune system destroys insulin-making cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels.
Insulin injections are required as a treatment
Symptoms-
- Thirst in extreme
- Increased hunger
- Dry mouth
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Upset stomach
- Frequent urination
- Mood swings
Graves’ Disease
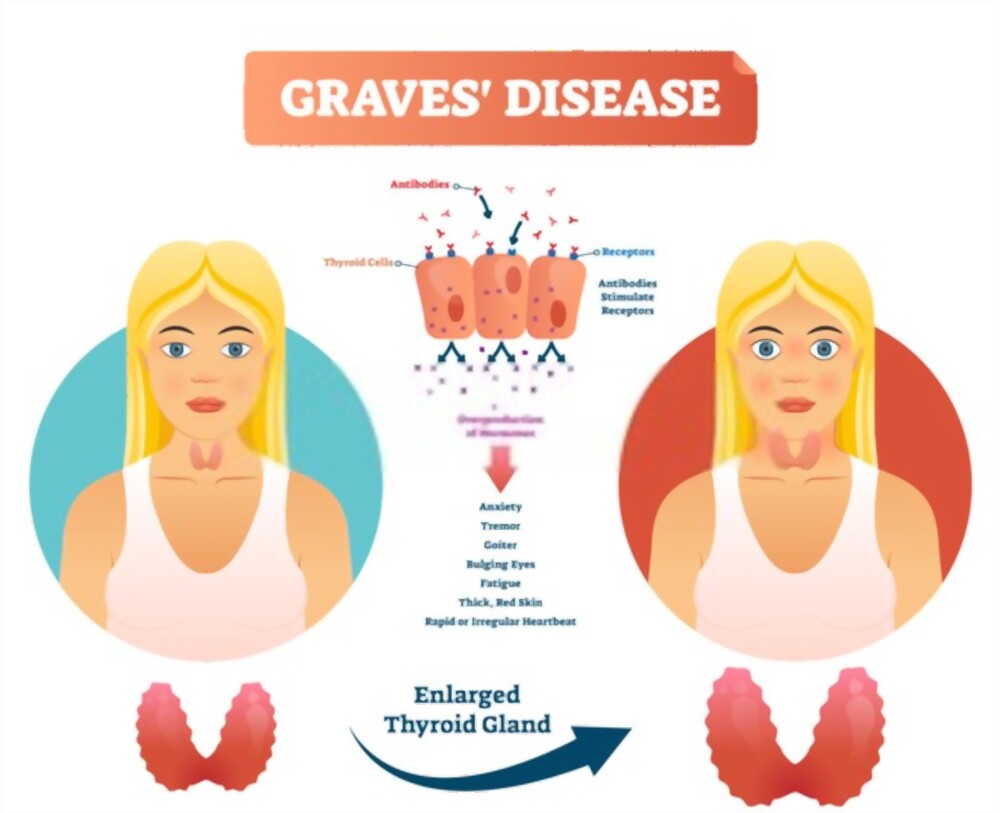
This disorder comprises an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
It is also known as Hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid hormones affect many-body systems. Therefore, it has a wide range of symptoms.
Symptoms-
- Irregular periods
- Weight loss
- Enlargement of thyroid gland (goiter)
- Bulging eyes
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Irregular heartbeat
- Irregular sleep
Psoriasis
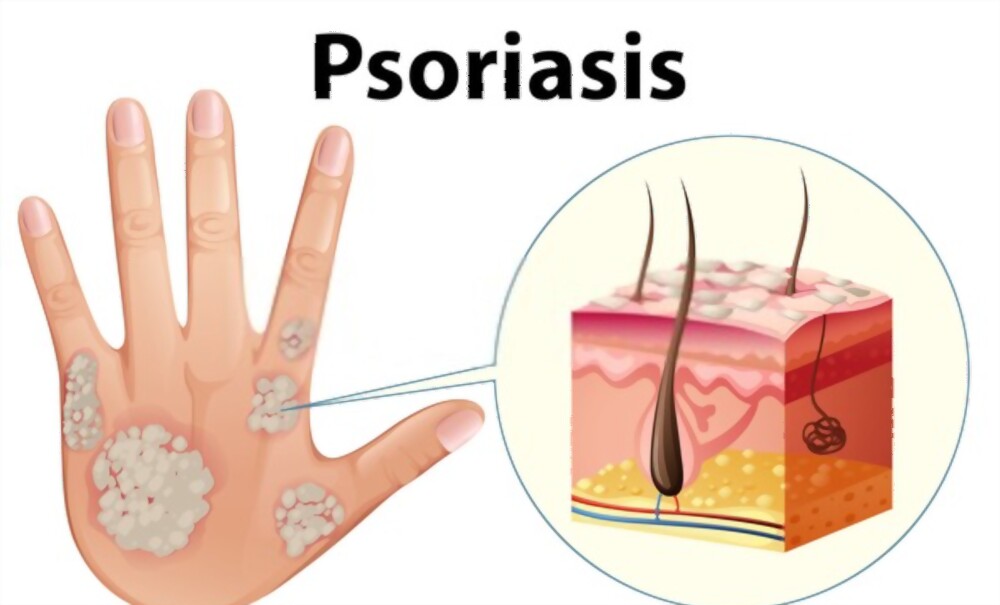
It is a skin disease – red, itchy patches commonly on knees, elbows, scalp, and trunk.
Immune system cells called T cells accumulate in the skin,
Skin cells reproduce rapidly.
Lupus
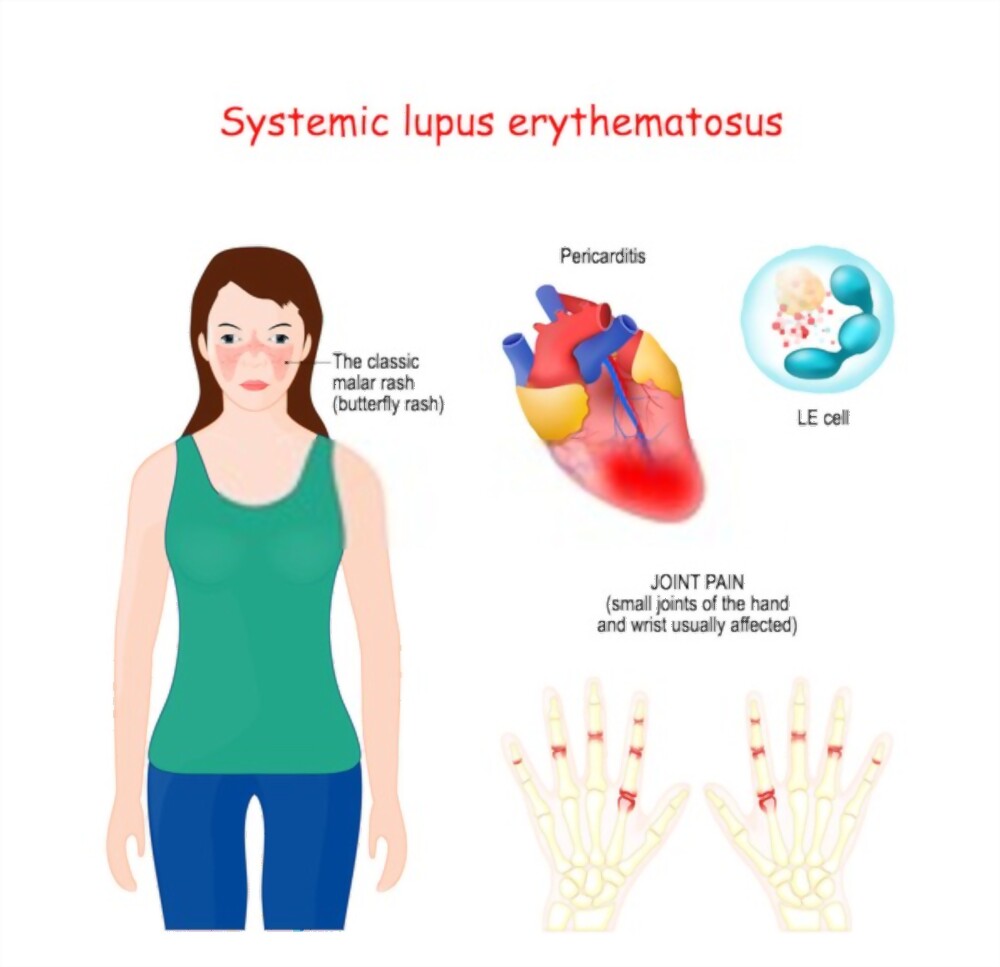
Autoimmune antibodies attach to tissues all over the body.
It is difficult to diagnose. Majorly because its symptoms overlap with those of other diseases.
Symptoms-
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Breathlessness or shortness of breath
- Dry eyes
- Headache
- Confusion
- Memory loss
- Butterfly-shaped rash on the face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose or rashes elsewhere on the body
- Skin lesions
Treatment of Auto-immune diseases
There is no particular treatment for auto-immune diseases.
Treatments can’t cure this kind of disease. They can only control the immune response.
Drugs prescribed-
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Immunosuppressive drugs
Prevention of Auto-Immune Diseases
- Maintain an anti-inflammatory diet.
- Maintain healthy weight (body mass index – BMI)
- Getting enough sleep
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a good gut health because gut contains microbes
Read More: Know all about Anemia- types, causes, prevention, etc. – V Cure (vcurehealthcare.com)